National Institutes of Health issued the following announcement on April 9.
NIH scientists develop macaque model to study Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever
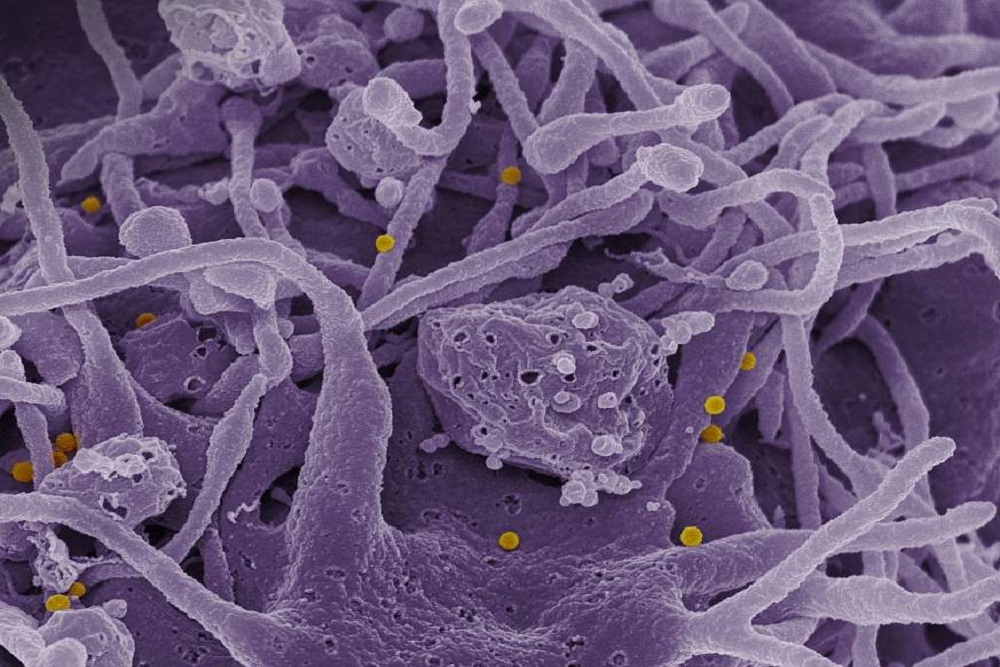
Scanning electron micrograph of CCHF viral particles (yellow) budding from the surface of cultured epithelial cells from a patient. NIAID
What
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral disease spread by ticks in the Middle East, Asia, Africa and parts of Europe. Infection with CCHF virus is fatal in nearly one of every three cases. No specific treatments or vaccines for CCHF exist, primarily because a suitable animal model for studying the disease has not been available. Scientists have used mice to study CCHF but had to weaken their immune systems to cause infection. Studies in larger animals have not consistently replicated human disease.
Now, as reported in Nature Microbiology, researchers have developed a new animal model to study the disease. Scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health, conducted a pilot study using CCHF virus to infect African green monkeys, rhesus macaques, and cynomolgus macaques. The strain of the virus they used, known as Kosova Hoti, was isolated from the blood of a person who died of CCHF. Most prior animal modeling studies had used a different viral strain isolated from a tick found in Nigeria.
The first two monkey species showed no signs of disease using various inoculation methods. Two of three cynomolgus macaques, however, developed disease. That led to a larger study of 12 cynomolgus macaques, four each inoculated under the skin, intravenously, or a combination of both. Within three days, all eight animals in the combination and intravenous groups showed signs of infection that led to severe disease. Two of the four animals inoculated under the skin developed mild signs of disease while the other two remained symptom-free.
Disease progression in the cynomolgus macaques followed the four phases that most infected people experience: 1) A 3- to 4-day incubation period; 2) a 3- to 5-day pre-hemorrhagic period; 3) a 2-to 3-day hemorrhagic period; and 4) recovery or death. Because their study included cynomolgus macaques that experienced a range of conditions, from no CCHF symptoms to severe disease, the scientists believe this animal model will be useful for examining how the infection progresses and interacts with the immune system. Ultimately, they plan to use the model to develop treatments and vaccines for CCHF.
Article
E Haddock, et al. A cynomolgus macaque model for Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever. Nature Microbiology DOI: 10.1038/s41564-018-0141-7 (2018).
Who
Heinz Feldmann, M.D., Ph.D., chief of NIAID’s Laboratory of Virology, is available to comment on this study.
Contact
To schedule interviews, please contact Ken Pekoc, (301) 402-1663, kpekoc@niaid.nih.gov(link sends e-mail).
NIAID conducts and supports research — at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide — to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
Original source can be found here.